The following information is for educational purposes only. The content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult your doctor for more information.

Ankle Pain
Ankle sprains happen when the ankle is rolled in or out in a forceful way that stretches or tears one or more of its ligaments. Symptoms can include: pain, swelling, weakness, bruising and difficulty walking or bearing weight. It is important that you treat an ankle sprain properly and quickly when it happens, this assures that you would have the best outcome preventing recurring sprains or even future ankle fractures. If you have experienced an ankle sprain, your foot and ankle doctor can help you treat the sprain so it would not become a chronic condition.
Athlete’s Foot and fungal nails
Athlete’s foot is a fungal infection of the skin. It most commonly involves the plantar skin of the foot. This kind of infection is picked up from the general environment and usually will respond well to topical prescription medication. The same class of fungus can also involve the nails and cause fungal nail infection. Fungal infection of the nails typically respond much better to oral anti-fungal medications but also can improve with the use of some topical treatments. Laser treatment of the nails is also available, and shows promising results for those who do not want to take the oral medications. The fungal infection of both nails and the skin tend to worsen with continuous use of shoes and socks, as the fungus grows more in moist and warm environments. Your Foot and ankle doctor can provide you with the best medical options to treat these infections.


Diabetic Foot Care
Diabetes is a chronic disease. Out of control diabetes can cause secondary issues throughout the body such as neuropathy (Abnormal sensation) of the lower extremities. This chronic involvement of the nerves can cause numbness and reduced sensation which makes the patient more prone to skin damage and infections. Your foot & ankle doctor you can help you protect your feet and avoid such problems.
Flat Feet in children and adults
This relatively common foot condition may be the root of many other related foot and ankle problems, such as bunions, hammertoes, heel pain, and even issues involving ankles, knees and the lower back. This condition arises from structural problems with the joints of the feet. If you believe you have issues with flat feet, your foot and ankle doctor could help you prevent or reduce the secondary effects that chronic flat feet could cause.…Although flat feet may be common in kids, in certain cases, the same structural issues can be present and may cause problems from an early ago. In these cases, the child may experience issues such as frequent falling, not wanting to run or play, or pain during activities. If you believe your child may be experiencing such problems, your foot and ankle doctor can help determine if your child would need any treatment.


Wound Care
There are various kinds of chronic wounds that can affect the lower legs, ankles and feet. Although there may be different causes for these wounds to develop, such as uncontrolled diabetes, numbness, circulation issues, or infections, often times they respond to treatment and can be resolved using various wound care techniques. Using our twenty years of experience in the field of wound care, we can help you control and resolve such wounds before they become chronic.
What is a Bunion Deformity?
Bunions ( Hallux abductovalgus ) are often described as a bump on the side of the big toe. But a bunion is more than that. The visible bump actually reflects changes in the bony framework of the front part of the foot. With a bunion, the big toe leans toward the second toe, rather than pointing straight ahead. Bunions are a progressive disorder.…
Bunions are most often caused by a faulty mechanical structure of the foot. Symptoms occur most often when wearing shoes that crowd the toes—shoes with a tight toe box or high heels. This may explain why women are more likely to have symptoms than men. In addition, spending long periods of time on your feet can aggravate the symptoms of bunions. Early treatments are aimed at easing the pain of bunions, but they won’t reverse the deformity itself.
Treatment options include: Changes in shoe-wear, Padding, Activity modifications, Medications, Icing, Injection therapy. ( Although rarely used) and Orthotic devices. Custom orthotic devices may be provided by your foot and ankle surgeon.
When the appearance, size or pain of a bunion interferes with daily activities, it’s time to discuss surgical options with your foot and ankle surgeon. Together you can decide if surgery is best for you. Recent advances in surgical techniques have led to a very good success rate in treating bunions. Benefits of Surgery include:
Less pain with walking & standing, Ability to fit into more narrow shoes, Ability to run and exercise with less discomfort, less or no pain and numbness, Prevention of future arthritis.


What is a Hammertoe?
Hammertoe is a contracture or bending of one or both joints of the second, third, fourth, or fifth (little) toes. This abnormal bending can put pressure on the toe when wearing shoes, causing problems to develop. Common symptoms of hammertoes include pain or irritation of the affected toe when wearing shoes. Even without corns and calluses, hammertoes can cause pain because the joint itself may become dislocated.…
Hammertoes usually start out as mild deformities and get progressively worse over time. If left untreated, hammertoes can become more rigid and will not respond to non-surgical treatment. Because of the progressive nature of hammertoes, they should receive early attention. Hammertoes never get better without some kind of intervention. Usually when the hammertoe has become more rigid, surgery is needed to relieve the pain and discomfort caused by the deformity. Often patients with hammertoe have bunions or other foot deformities corrected at the same time. The length of the recovery period will vary, depending on the procedure or procedures performed.
Treatment options include: Changes in shoe-wear, Padding, Activity modifications, Medications, Icing, Injection therapy. ( Although rarely used) and Orthotic devices. Custom orthotic devices may be provided by your foot and ankle surgeon.
When the appearance, size or pain of a bunion interferes with daily activities, it’s time to discuss surgical options with your foot and ankle surgeon. Together you can decide if surgery is best for you. Recent advances in surgical techniques have led to a very good success rate in treating bunions. Benefits of Surgery include:
Less pain with walking & standing, Ability to fit into more narrow shoes, Ability to run and exercise with less discomfort, less or no pain and numbness, Prevention of future arthritis.
What is Plantar Fasciitis?
Plantar fasciitis is an inflammation of the band of tissue (the plantar fascia) that extends from the heel to the toes. In this condition, the fascia first becomes irritated and then inflamed-resulting in heel pain.
The symptoms of plantar fasciitis are: Pain on the bottom of the heel, Pain that is usually worse upon arising, Pain that increases over a period of months. …
People with plantar fasciitis often describe the pain as worse when they get up in the morning or after they’ve been sitting for long periods of time. After a few minutes of walking the pain may decrease, because walking stretches the fascia. So for some people the pain subsides but returns after spending long periods of time on their feet.
The most common cause of plantar fasciitis relates to instability in the structure of the foot. For example, people who have problems with their arches—either overly flat feet or high-arched feet—are more prone to developing plantar fasciitis.
Wearing non-supportive footwear on hard, flat surfaces puts abnormal strain on the plantar fascia and can also lead to plantar fasciitis. This is particularly evident when a person’s job requires long hours on their feet. Obesity also contributes to plantar fasciitis.
Placing soft pads in the shoe softens the impact of walking. Strapping of the arch helps support the foot and reduce strain on the fascia. Custom orthotic devices that fit into your shoe help correct the underlying structural abnormalities that cause the plantar fasciitis.
In some cases, corticosteroid injections are used to help reduce the inflammation and relieve pain. In some cases. Exercises and other physical therapy measures may be used to help provide relief.

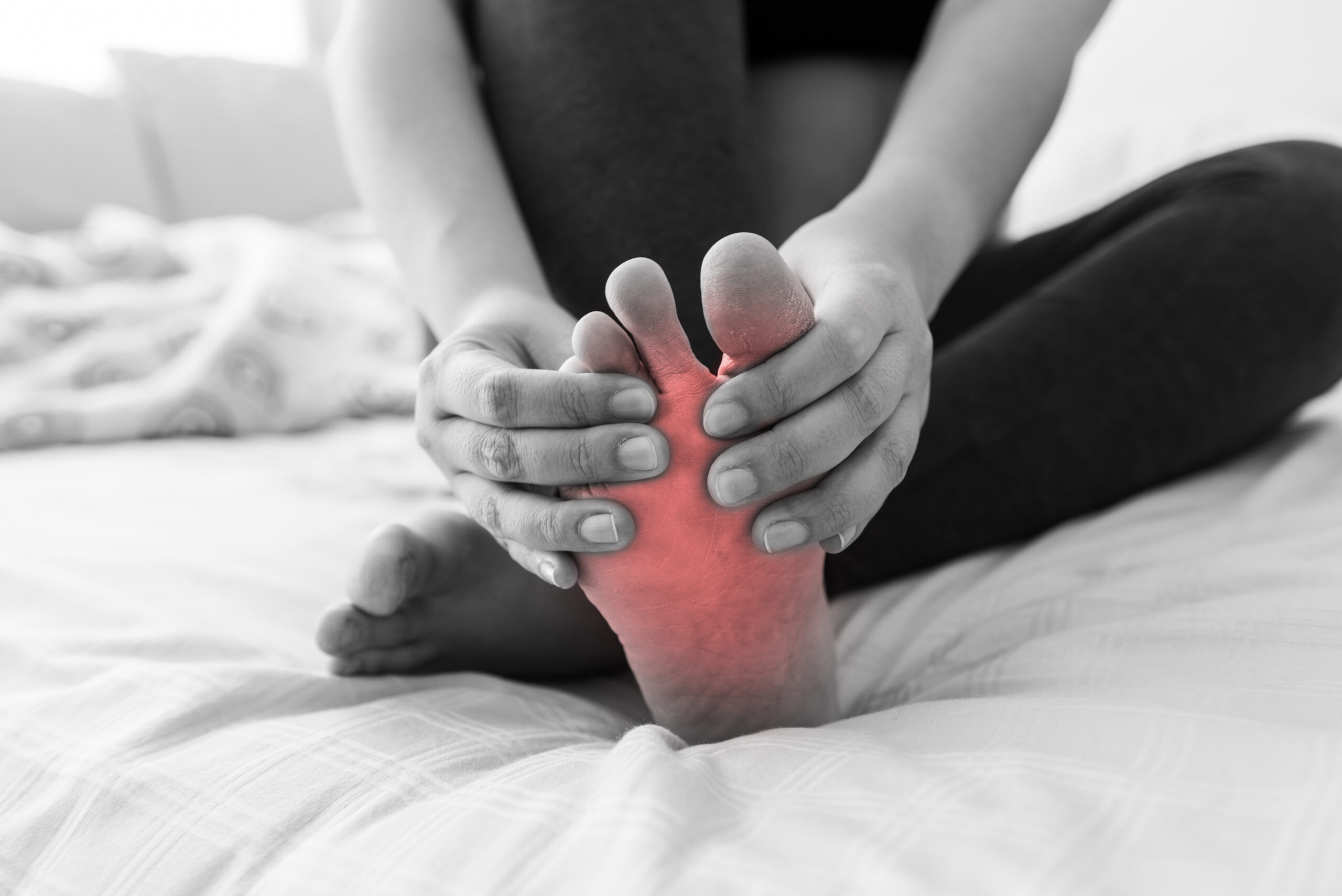
What is a Neuroma?
A neuroma is a thickening of nerve tissue that may develop in various parts of the body. The most common neuroma in the foot is a Morton’s neuroma, which occurs at the base of the third and fourth toes.…
The thickening, or enlargement, of the nerve that defines a neuroma is the result of compression and irritation of the nerve. This compression creates swelling of the nerve, eventually leading to permanent nerve damage. If you have a Morton”s neuroma, you will probably have one or more of these symptoms where the nerve damage in occurring: Tingling, burning, or numbness , Pain , A feeling that something is inside the ball of the foot, or that there’s a rise in the shoe or your sock is bunched up. The progression of a Morton’s neuroma often follows this pattern: The symptoms begin gradually. At first they occur only occasionally, when wearing narrow-toed shoes or performing certain aggravating activities. The symptoms may go away temporarily by massaging the foot or by avoiding aggravating shoes or activities. Over time the symptoms progressively worsen and may persist for several days or weeks.
The symptoms become more intense as the neuroma enlarges and the temporary changes in the nerve become permanent.
Anything that causes compression or irritation of the nerve can lead to the development of a neuroma. One of the most common offenders is wearing shoes that have a tapered toe box, or high-heeled shoes that cause the toes to be forced into the toe box. People with certain foot deformities—bunions, hammertoes, flatfeet, or more flexible feet—are at higher risk for developing a neuroma. If there is no significant improvement after initial treatment, injection therapy may be tried. Surgery may also be considered in patients who have not received adequate relief from other treatments.
What is a Tailor’s Bunion?
Tailor’s bunion, also called a bunionette, is an enlargement of the fifth metatarsal bone at the base of the little toe. The metatarsals are the five long bones of the foot. The enlargement that characterizes a tailor’s bunion occurs at the metatarsal “head,” located at the far end of the bone where it meets the toe. Tailor’s bunions are not as common as bunions, which occur on the inside of the foot, but both are similar in symptoms and causes. The symptoms of tailor’s bunions include redness, swelling, and pain at the site of the enlargement. These symptoms occur when wearing shoes that rub against the enlargement, irritating the soft tissues underneath the skin and producing inflammation.…
Often a tailor’s bunion is caused by a faulty mechanical structure of the foot. In these cases, changes occur in the foot’s bony framework that result in the development of an enlargement. The fifth metatarsal bone starts to protrude outward, while the little toe moves inward. This shift creates a bump on the outside of the foot that becomes irritated whenever a shoe presses against it. Regardless of the cause, the symptoms of a tailor’s bunion are usually aggravated by wearing shoes that are too narrow in the toe, producing
constant rubbing and pressure. In fact, wearing shoes with a tight toe box can make the deformity get progressively worse.
Often a tailor’s bunion is caused by a faulty mechanical structure of the foot. In these cases, changes occur in the foot’s bony framework that result in the development of an enlargement. The fifth metatarsal bone starts to protrude outward, while the little toe moves inward. This shift creates a bump on the outside of the foot that becomes irritated whenever a shoe presses against it. Regardless of the cause, the symptoms of a tailor’s bunion are usually aggravated by wearing shoes that are too narrow in the toe, producing
constant rubbing and pressure. In fact, wearing shoes with a tight toe box can make the deformity get progressively worse.
Surgery is often considered when pain continues despite conservative care. Surgery is highly successful in the treatment of tailor’s bunions.

